This is a note from WHY IS THE HEAP SO SLOW?
System Calls
System calls are the apis provided by the operating system and we use them to request some service which only the operating system can do. System calls can be expensive in terms of performance.
When a program is executed, it receives a new name, a process. A process has its own state stored in CPU through register.
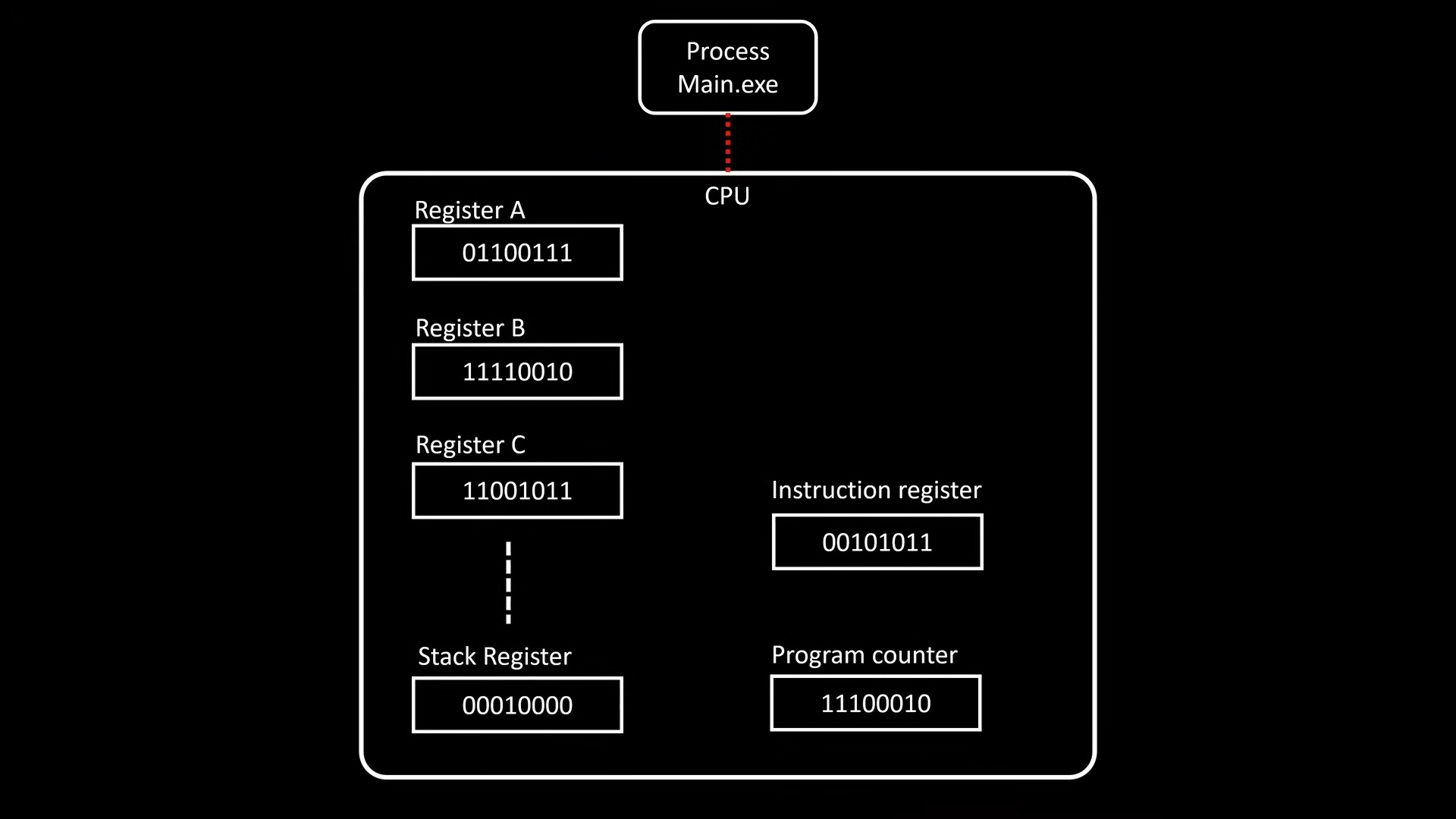
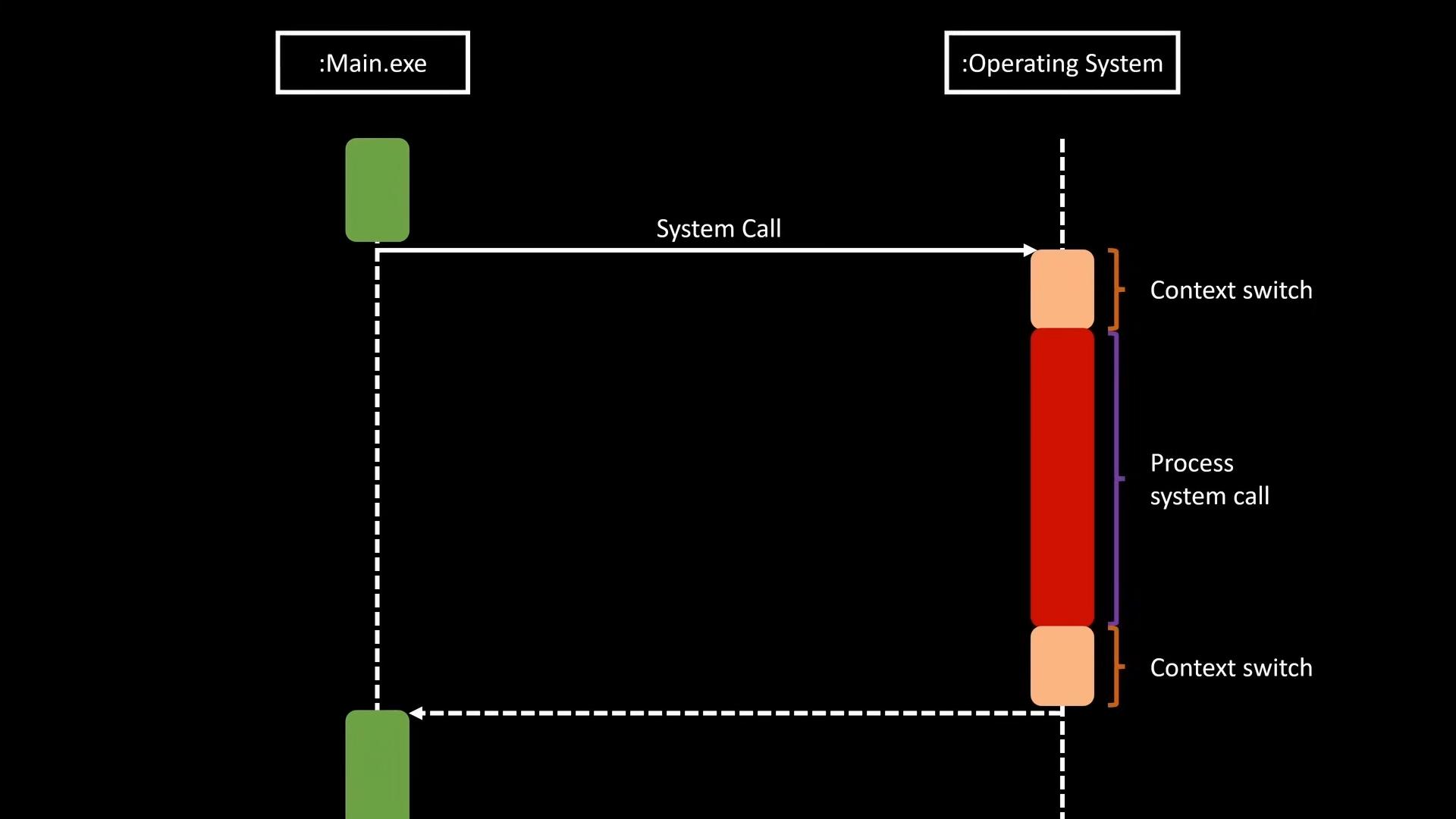
When the process makes a system call, the OS needs to use the CPU to serve the request. However, it cannot use the CPU directly, since it has the state of our process. OS will take a snapshot of the state and put it into the memory. Then restore it after execution of the request. Such behavior is called context switch, and context switch takes time and resources.
Memory Layout
The issue with the heap is that its hard to avoid memory fragmentation, and when memory fragmentation occurs, we need system calls to request for another chunk of memory.
For example, a server that can receive images from users and return black and white filter of the image to the users, and it is designed to handle multiple clients concurrently.
When the server receives images, it spawns threads for each image. Smaller images are processed more quickly, and as soon as these smaller images are processed, the memory for these images are no longer needed, causing fragmentation on the heap.
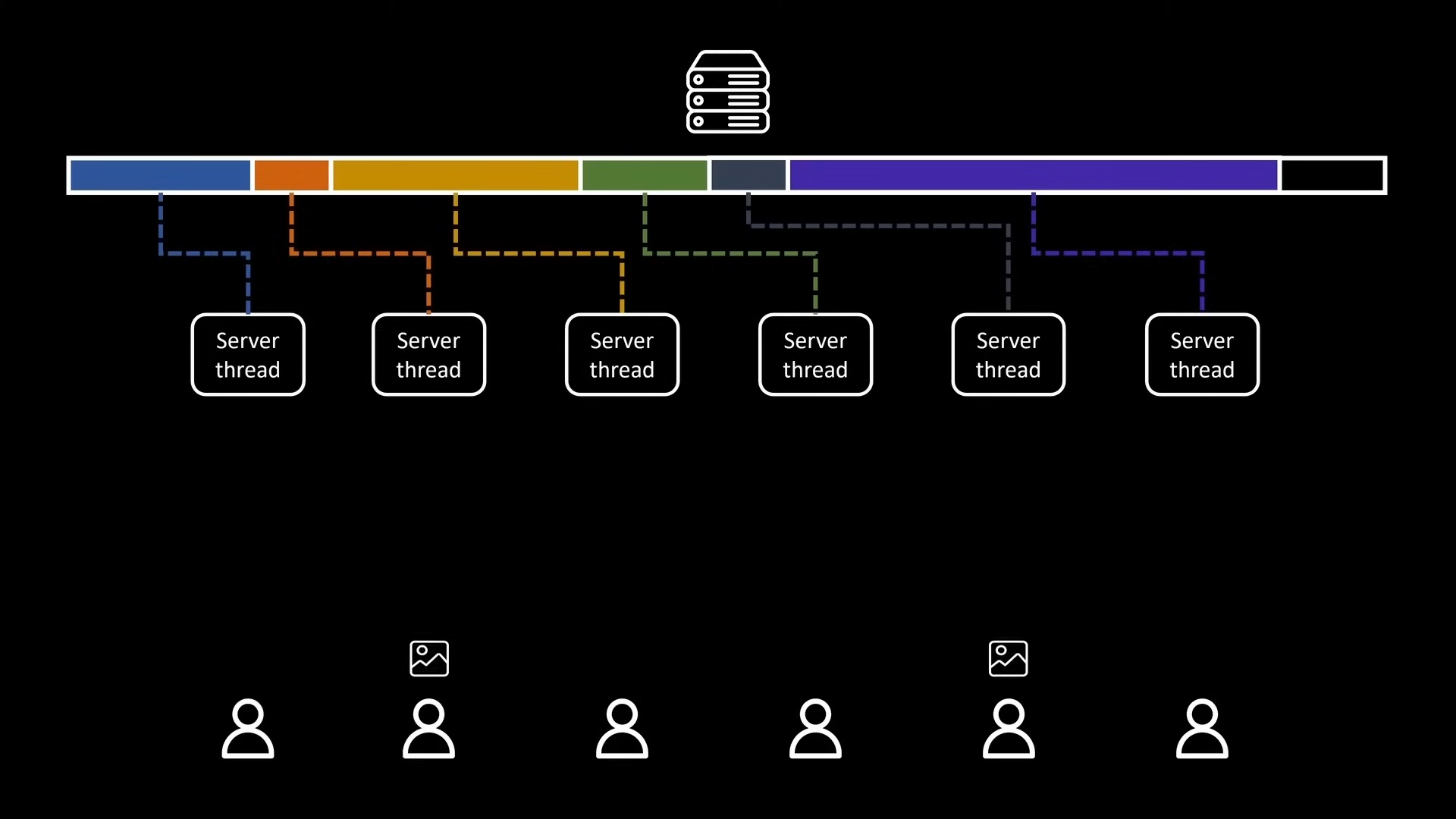
When we need to store more data in the heap, to avoid system calls, there are different ways to utilize the heap.
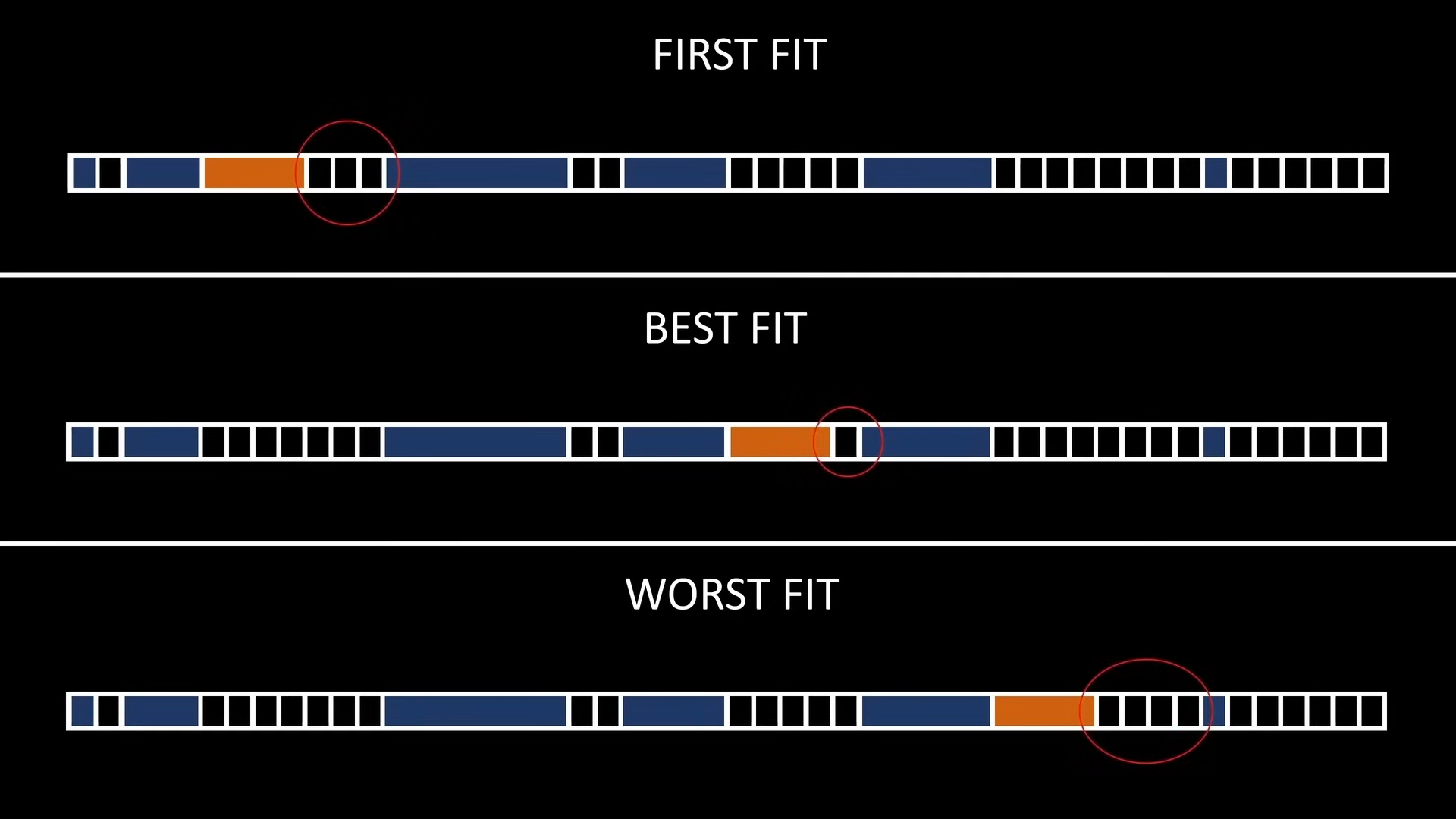
- First fit: choose the first hole that is large enough to accommodate our value
- Best fit: choose the smallest hole that is still large enough for our value
- Worst fit: choose the largest available hole where our value can fit
Conclusion
Pros
- Dynamic size
- Large memory allocations
- Fast accessing times if used correctly
Cons
- Performance penalties
- Allocations require searching available sub-regions within the heap
- Allocation may require a System Call
- Runtime errors
- Memory leaks
- Null pointers dereferences
- Dangling pointers
- Performance penalties
The heap itself is actually not slow, we say its slow because of the whole process of allocatiing memory is slow. If heap is allocated properly, it is as fast as stack, since they are both in the ram.